Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
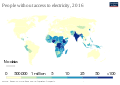
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
Climate Change 2007, the fourth report of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to evaluate the risks of global warming since 1990, is being published in sections throughout 2007. Prior to publishing, the report - which is the combined work of hundreds of experts - is reviewed by representatives from many of the world's governments.
Due to the accumulation of evidence, the report goes further than previous reports by stating that 'warming of the climate system is unequivocal'. It goes on to say that 'most of the observed increase in globally averaged temperatures since the mid-20th century is 'very likely' due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations'. Fossil fuel use is given as the primary source of the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide, with the increase in methane being very likely caused by a combination of agricultural practices and fossil fuel use.
Based on an analysis of computer climate models, the report states that average surface temperatures will rise during this century, most likely between 1.1 to 4.3°C (5.2 to 11.5 °F), depending on the mitigation actions taken. Excluding the effects of ice sheet flow, they also predict a sea level rise of 18 to 26 cm (7 to 23 inches), more heat waves and more heavy rain. An increase in areas affected by droughts, in the intensity of tropical cyclones and in extreme high tides is also likely. The IPCC believe that stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations is possible at a reasonable cost, with stabilization between 445 and 535 ppm costing less than 3% of global GDP. They do warn, however, that a 'large shift in the pattern of investment' is required.
Selected image

Photo credit: From an image by Wolfgang Beyer
Strombolian volcanic eruptions can eject incandescent cinder, lapilli and lava bombs to altitudes of tens to hundreds of meters.
Did you know?
- The development of renewable energy in Iceland means that by 2050 the country should be the world's first zero-carbon economy?
- World's two largest oil shale-fired power plants (Narva Power Plants) generate more than 90% of power in Estonia?
- NW Natural in Portland, Oregon was the first gas company in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States when it started in 1859?
- The Assistant Secretary of Energy for Fossil Energy is responsible for America's Strategic Petroleum Reserve?
- Despite declines in production in recent years, Victoria still produces almost 20% of Australia's crude oil?
- 4.26 million tonnes of the Sun are converted to energy every second by nuclear fusion?
- The first gasworks in the United Kingdom was built by the Gas Light and Coke Company, incorporated by Royal Charter in 1812?
- The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline was a central plot point in the James Bond film The World Is Not Enough?
Selected biography
Born in Ireland, Thomson studied at the University of Glasgow, Scotland. On graduating, he became a mathematics teacher at the Royal Belfast Academical Institution. During his life Thomson published more than 600 scientific papers and filed over 70 patents.
As early as 1845 Thomson pointed out that the experimental results of William Snow Harris were in accordance with the laws of Coulomb. Over the period 1855 to 1867, Thomson collaborated with Peter Guthrie Tait the Treatise on Natural Philosophy that unified the various branches of physical science under the common principle of energy. His inventions included the current balance for the precise specification of the ampere, the standard unit of electric current.
In 1893, Thomson headed an international commission to decide on the design of the Niagara Falls power station. Despite his previous belief in the superiority of direct current electric power transmission, he agreed to use alternating current after seeing a Westinghouse demonstration at the Chicago World's Fair.
General images
Quotations
- "In recent years, new nations have entered enthusiastically into industrial production, thereby increasing their energy needs. This has led to an unprecedented race for available resources. Meanwhile, some parts of the planet remain backward and development is effectively blocked, partly because of the rise in energy prices. What will happen to those peoples?" – Pope Benedict XVI, 2007
- "In order to prevent the harmful consequences that crude oil price volatility is having on the well-being of our people, it is urgent that we convene a World Leaders Summit to present alternative solutions to this serious problem, which could quite possibly be a significant shock to the prosperity of developing nations." – Leonel Fernández, 2005
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
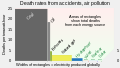
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
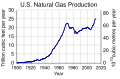
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
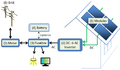
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus