Šinuḫtu
Šinuḫtu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early 1st millennium BCE ?–718 BCE | |||||||||
 Šinuḫtu among the Syro-Hittite states | |||||||||
| Capital | Šinuḫtu 38°22′27″N 34°01′44″E / 38.374167°N 34.028889°E | ||||||||
| Common languages | Luwian | ||||||||
| Religion | Luwian religion | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
• r. unknown – 718 BCE | Kiyakiyas | ||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||
• Established | Early 1st millennium BCE ? | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 718 BCE | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Turkey | ||||||||
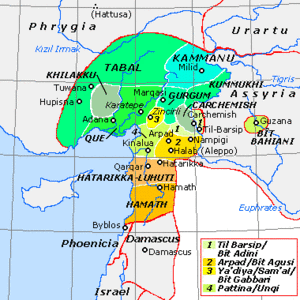
Šinuḫtu (Neo-Assyrian Akkadian: 𒌷𒅆𒉡𒄴𒌅 and 𒌷𒅆𒉡𒄴𒌓[1]) was a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite state which existed in the region of Tabal in southeastern Anatolia in the Iron Age.
Location[edit]
Šinuḫtu was located on the site of what is now Aksaray in Turkey,[2][3][4] immediately to the south-east of Lake Tuz,[5] and consisted of its capital city and a small territory surrounding it.[6]
The neighbours of Šinuḫtu were Atuna to its north, and Tabal proper to the east.[6]
History[edit]
The kingdom of Šinuḫtu might have come into existence during the early 1st millennium BCE, and one of the state's early kings might have been one of the 24 kings of the Tabalian region who offered tribute to the Neo-Assyrian king Shalmaneser III (r. 859 – 824 BCE) during his campaign there in 837 BCE.[6]
By c. 738 BC, the Tabalian region, including Šinuḫtu, had become a tributary of the Neo-Assyrian king Tiglath-pileser III (r. 745 – 727 BCE), possibly after his conquest of Arpad over the course of 743 to 740 BC caused the states of the Tabalian region to submit to him, or possibly as a result of a campaign of Tiglath-pileser III in Tabal.[7][8][9]
The only known ruler of Šinuḫtu was the late 8th century BCE king Kiyakiyas, who was a tributary state of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. According to an inscription of Kiyakiyas dedicated to the storm-god Tarḫunzas, Šinuḫtu appears to have been a thriving state at this time.[2][6]
The king Wasusarmas of Tabal claimed that Kiyakiyas was one of the three rulers who had helped him defeat an coalition of eight enemy rulers.[10][6][11]
Following the union of the Phrygians and the Muški under the king Midas, his Phrygian kingdom became a major rival to Neo-Assyrian power in eastern Anatolia, and the region of Tabal became contested between the Neo-Assyrian and Phrygian empires.[12]
Midas tried to convince the still independent local rulers of Tabal to switch their allegiances to Phrygia, and several of them accepted his offer,[12] with Kiyakiyas soon breaking his oath of allegiance to the Neo-Assyrian Empire and withholding his tribute, possibly after having been incited to do so by the Phrygian king Midas.[2][13][6]
The Neo-Assyrian king Sargon II (r. 722 – 705 BC) reacted through cautionary action meant to deter the other Tabalian kingdoms from rebelling[5] by invading Šinuḫtu in 718 BCE and deporting Kiyakiyas, his family and warriors, and 7350 inhabitants of the kingdom's capital city to Assyria, where Kiyakiyas himself was executed by being burnt alive.[2][13][10][9][14][4][15]
Sargon II then abolished the kingdom of Šinuḫtu and handed its territory to the king Kurdis of the nearby state of Atuna.[2][16][6][5][4][15]
List of kings of Šinuḫtu[edit]
- Kiyakiyas (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔗳𔓱𔗳𔓱𔗔;[17][18] Neo-Assyrian Akkadian: 𒁹𒆠𒀝𒆠, romanized: Kiakki;[19] r. unknown – 718 BCE)
References[edit]
- ^ "Šinuhtu [1] (SN)". Textual Sources of the Assyrian Empire. Open Richly Annotated Cuneiform Corpus. Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
- ^ a b c d e Bryce 2009, p. 644.
- ^ Weeden 2010, p. 56.
- ^ a b c Weeden 2017, p. 725.
- ^ a b c Bryce 2012, p. 278.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bryce 2012, p. 148.
- ^ Bryce 2012, p. 144.
- ^ Bryce 2012, p. 271.
- ^ a b Aro 2013, p. 389.
- ^ a b Weeden 2010, p. 50.
- ^ Weeden 2017, p. 724.
- ^ a b Bryce 2009, p. 685.
- ^ a b Weeden 2010, p. 42.
- ^ Aro 2023, p. 117.
- ^ a b Baker 2023, p. 302.
- ^ Weeden 2010, p. 41.
- ^ Hawkins 2000b, p. 476.
- ^ Hawkins 2000c, p. 475.
- ^ "Kiakki [KING OF ŠINUHTU] (RN)". Textual Sources of the Assyrian Empire. Open Richly Annotated Cuneiform Corpus. Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
Bibliography[edit]
- Aro, Sanna (2013). "Tabal". In Streck, Michael P. [in German]; Frantz-Szabó, Gabriella; Krebernik, Manfred [in German]; Bonacossi, D. Morandi; Postgate, J. N.; Seidl, Ursula [in German]; Stol, M.; Wilhelm, Gernot [in German] (eds.). Reallexikon der Assyriologie und Vorderasiatischen Archäologie (in German). Vol. 13. Berlin, Germany; New York City, United States: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-110-30715-3.
- Aro, Sanna (2023). "Vanishing kingdoms: Tabal and Tuwana during the seventh century BC". In Draycott, Catherine M.; Branting, Scott; Lehner, Joseph W.; Özarslan, Yasemin (eds.). From Midas to Cyrus and Other Stories: Papers on Iron Age Anatolia in Honour of Geoffrey and Françoise Summers. BIAA Monograph Series. London, United Kingdom: British Institute at Ankara. pp. 113–135. ISBN 978-1-912-09011-2.
- Baker, Heather D. (2023). "The Assyrian Empire: A View from Within". In Radner, Karen; Moeller, Nadine; Potts, Daniel T. (eds.). The Age of Assyria. The Oxford History of the Ancient Near East. Vol. 4. New York City, United States: Oxford University Press. pp. 257–351. ISBN 978-0-190-68763-2.
- Bryce, Trevor (2009). The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia: From the Early Bronze Age to the Fall of the Persian Empire. London, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-39485-7.
- Bryce, Trevor (2012). The World of The Neo-Hittite Kingdoms: A Political and Military History. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-199-21872-1.
- Hawkins, John David [in German] (2000b). Inscriptions of the Iron Age, Part 2: Text: Amuq, Aleppo, Hama, Tabal, Assur Letters, Miscellaneous, Seals, Indices. Corpus of Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Vol. 1. Berlin, Germany; New York City, United States: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-110-10864-4.
- Hawkins, John David [in German] (2000c). Inscriptions of the Iron Age, Part 3: Plates. Corpus of Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscriptions. Vol. 1. Berlin, Germany; New York City, United States: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-110-10864-4.
- Weeden, Mark (2010). "Tuwati and Wasusarma: Imitating the Behaviour of Assyria". Iraq. 72. British Institute for the Study of Iraq: 39–61. doi:10.1017/S0021088900000589. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- Weeden, Mark (2017). "Tabal and the Limits of Assyrian Imperialism". In Heffron, Yağmur; Stone, Adam; Worthington, Martin (eds.). At the Dawn of History: Ancient Near Eastern Studies in Honour of J. N. Postgate. Vol. 2. Winona, United States: Eisenbrauns. p. 721-736. ISBN 978-1-57506-471-0.